Wed, Jan 1, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 17, Issue 4 (December 2020)
IJMSE 2020, 17(4): 1-9 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
karimzadeh S, Mahboubi F, Daviran G. Plasma Nitriding Behavior of DIN 1.2344 Hot Work Tool Steel. IJMSE 2020; 17 (4) :1-9
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-1592-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-1592-en.html
Abstract: (10739 Views)
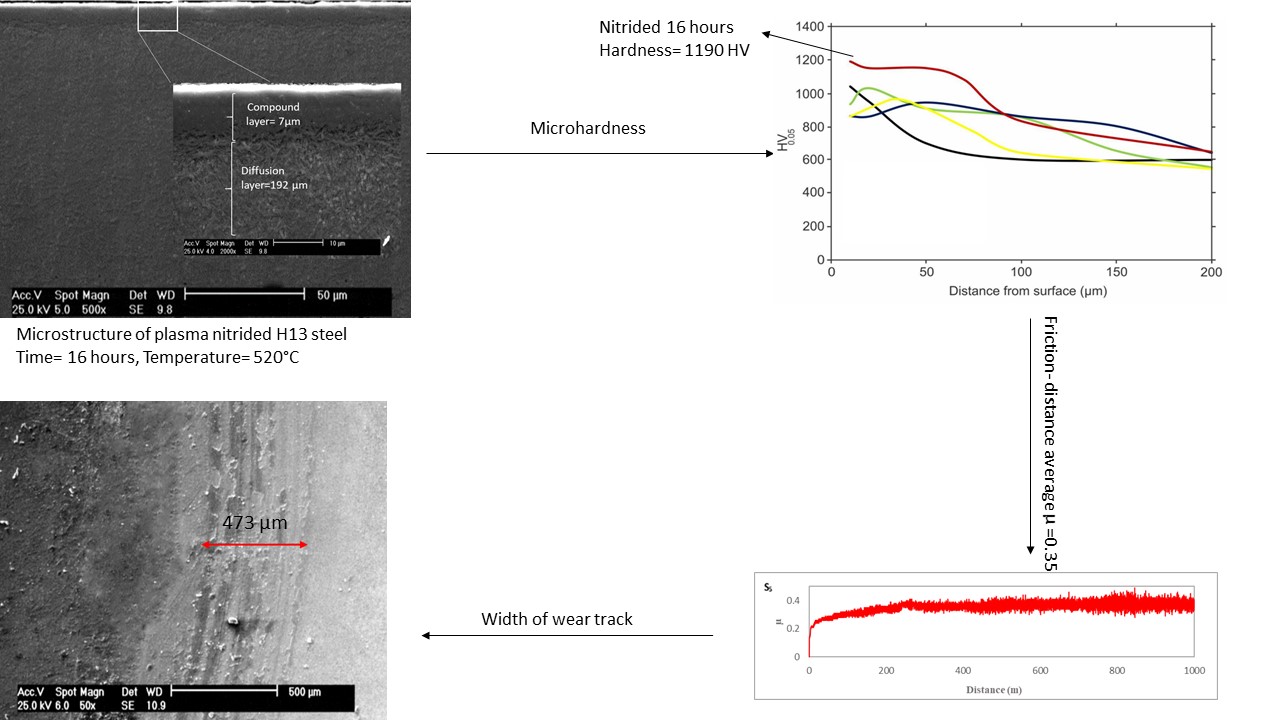
In the present investigation effects of time and temperature on plasma nitriding behavior of DIN 1.2344 (AISI H13) steel are studied. Pulsed plasma nitriding process with a gas mixture of N2 = 25% + H2 = 75% and duty cycle of 70% is applied to cylindrical samples of DIN 1.2344 hot work tool steel. X-ray diffraction, surface roughness, microhardness and ball on disc wear test are performed and behavior of plasma nitrided samples are compared. Scanning electron microscopy and optical microscopy are used in order to observe the microstructure of samples after nitriding. XRD results showed that the compound layer is dual phase. Hardness near the surface dropped by rising the process temperature and it rose in longer process durations. The comparison of µ results showed frictional properties in longer durations with lower temperatures is approximately the same in higher temperatures with shorter durations.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Surfe coating and corrosion
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |