Sun, Jun 8, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 20, Issue 3 (September 2023)
IJMSE 2023, 20(3): 1-15 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Mariani F E, Viana Figueiredo G, Barragan G, Castelleti L C, Teixeira Coelho R. Hardness and Wear Characteristics of Laser-Clad WC-17Co Coatings on AISI H13 and AISI 4140 Steel. IJMSE 2023; 20 (3) :1-15
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3206-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3206-en.html
Fabio Edson Mariani 
 , Gabriel Viana Figueiredo
, Gabriel Viana Figueiredo 
 , German Barragan
, German Barragan 
 , Luiz Carlos Castelleti
, Luiz Carlos Castelleti 
 , Reginaldo Teixeira Coelho
, Reginaldo Teixeira Coelho 


 , Gabriel Viana Figueiredo
, Gabriel Viana Figueiredo 
 , German Barragan
, German Barragan 
 , Luiz Carlos Castelleti
, Luiz Carlos Castelleti 
 , Reginaldo Teixeira Coelho
, Reginaldo Teixeira Coelho 

Abstract: (11466 Views)
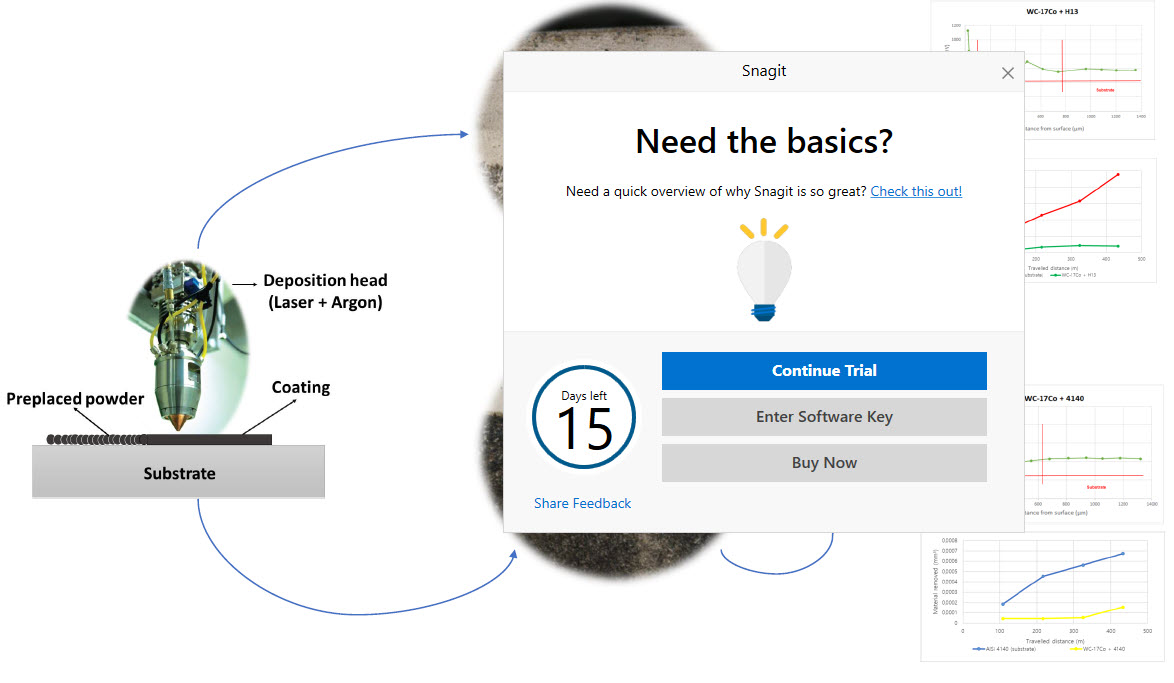
Elevating component performance through advanced surface coatings finds its epitome in the domain of laser cladding technology. This technique facilitates the precision deposition of metallic, ceramic, or cermet coatings, accentuating their superiority over conventional methods. The application spectrum for laser-clad metallic coatings is extensive, encompassing critical components. Central to the efficacy of laser cladding is the modulation of laser parameters—encompassing power, speed, and gas flow—which decisively influence both process efficiency and coating properties. The meticulous calibration of these parameters holds the key to producing components endowed with refined attributes while ensuring the sustainable continuation of the process. As such, this study embarks on an empirical investigation aimed at transcending existing process limitations. It delves into the characterization of laser-clad WC-17Co coatings on AISI H13 and AISI 4140 steels. The importance of WC-17Co coatings lies in their capacity to enhance wear resistance, extend component life, reduce maintenance costs, and improve the performance of various industrial components across diverse sectors. On the other hand, the substrates have pivotal roles. AISI H13 is lauded for its exceptional hot work capabilities, while AISI 4140 steel is renowned for its robust strength and endurance. Through rigorous evaluation, the resultant deposited coatings offer crucial insights into the efficacy of manufacturing parameters. Employing a comprehensive suite of analytical techniques including laser confocal microscopy, Vickers microhardness assessment, and micro-adhesive wear testing, the study thoroughly characterizes the samples. The outcomes underscore the achievement of homogenous coatings marked by elevated hardness and exceptional wear resistance, thereby signifying a substantial enhancement over the substrate materials.
Type of Study: Technical Note |
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |