BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-912-en.html
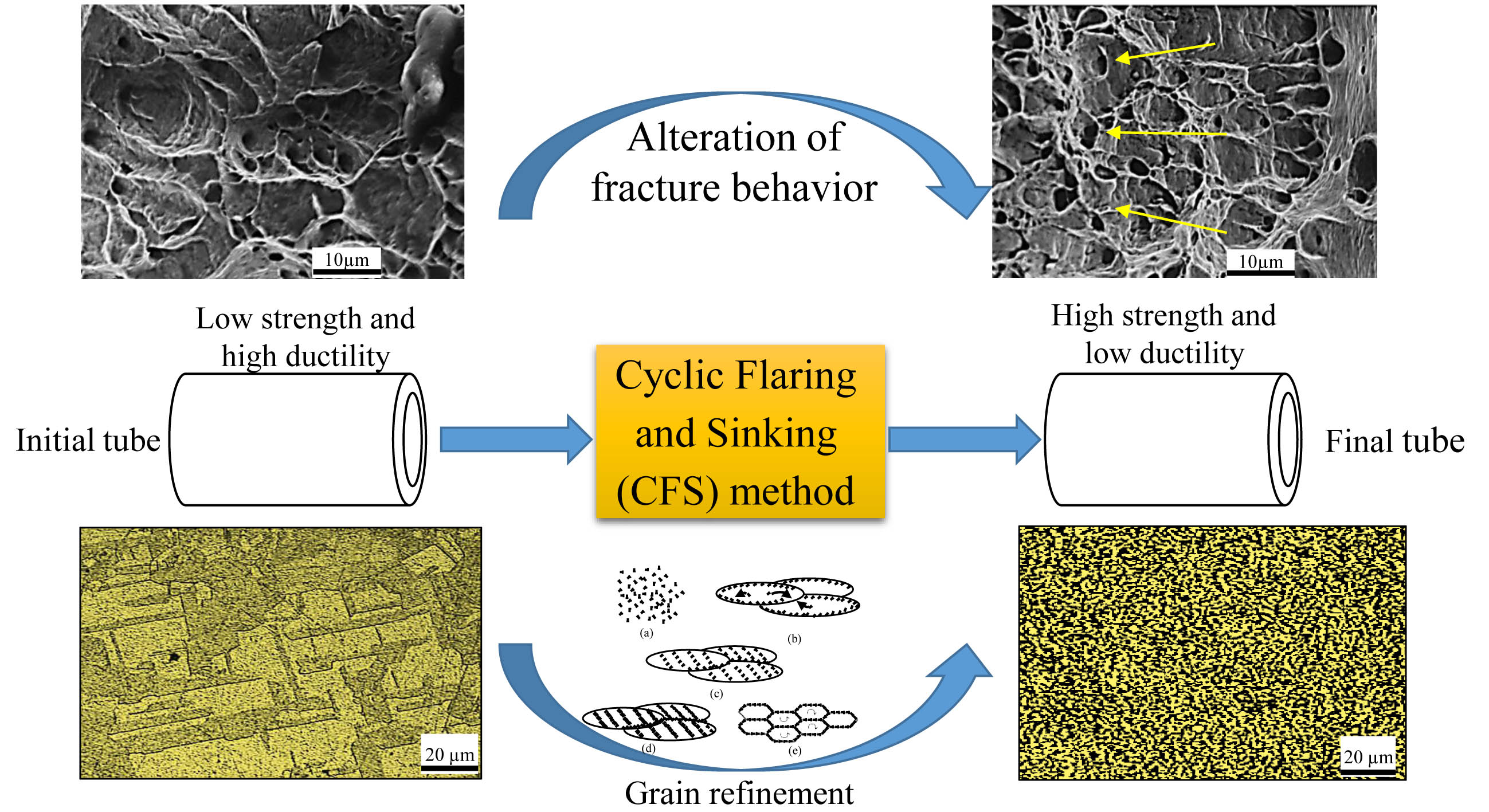
In this paper, cyclic flaring and sinking (CFS) as a new severe plastic deformation (SPD) method was employed to produce the ultrafine grain (UFG) copper tubes. The extra friction has eliminated in the CFS method that provided the possibility for production of longer UFG tubes compared to the other SPD methods. This process was done periodically to apply more strain and consequently finer grain size and better mechanical properties. The CFS was performed successfully on pure copper tubes up to eleven cycles. Mechanical properties of the initial and processed tubes were extracted from tensile tests in the different cycles. The remarkable increase in strength and decrease in ductility take placed in the CFS-ed tubes. The material flow behavior during CFS processing was analyzed by optical microscopy (OM), and a model was presented for grain refinement mechanism of pure copper based on multiplication and migration of dislocations (MMD). This mechanism caused that the initial grains converts to elongated dislocation cells (subgrains) and then to equiaxed ultrafine grains in the higher cycles. The CFS method refined the microstructure to fine grains with the mean grain size of 1200nm from initial coarse grain size of 40µm
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |